Table of Contents Show
High purity silicon metal is a cornerstone of modern technology. It’s used in everything from smartphones to solar panels. But how is this essential material made? Let’s break down the process.
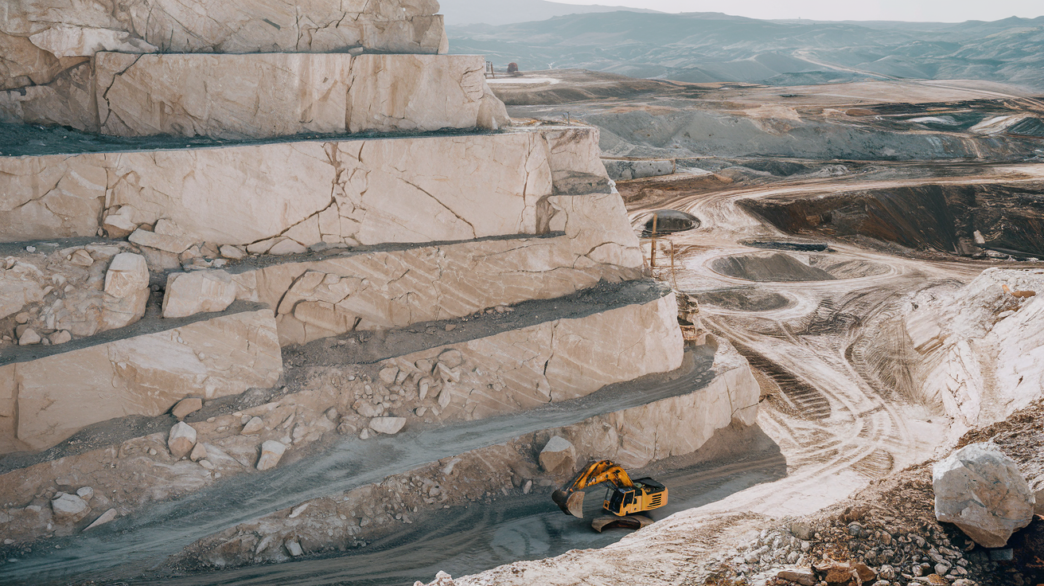
The Raw Materials
It all starts with quartzite. This rock is abundant in the Earth’s crust and rich in silica (SiO2). Miners extract it through open-pit operations. In 2023, global silicon metal production hit about 8 million metric tons. China led the pack, producing around 5.4 million tons.

The Reduction Process
This is where things heat up – literally. The quartzite goes into electric arc furnaces. These massive units reach temperatures over 2,000°C. Here’s the basic reaction:
SiO2 + 2C → Si + 2CO
But it’s not that simple. Achieving high purity requires precise control. The industry standard for “high purity” is typically 99.99% (4N) or higher.
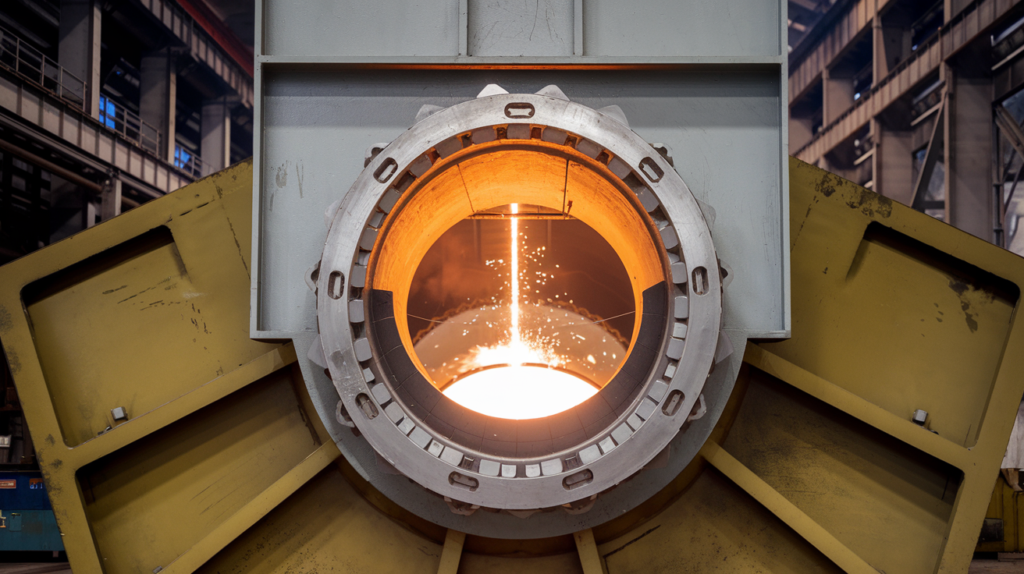

Refining for Higher Purity
The initial process gives us metallurgical-grade silicon, about 98-99% pure. To get higher purities, we need extra steps:
- Acid Leaching: This removes metallic impurities.
- Directional Solidification: As the silicon cools, impurities tend to separate out.
- Float Zone Refining: For the highest purities (up to 11N), a molten zone is passed through a silicon ingot multiple times.
Recent tech advances have boosted efficiency. AI-driven furnace control systems, for instance, have increased energy efficiency by 5-7% and silicon yield by 3%.

Market Trends
The high purity silicon metal market is growing fast. Projections show a 6.8% CAGR from 2024 to 2030. What’s driving this? Mainly demand from semiconductor and solar industries.
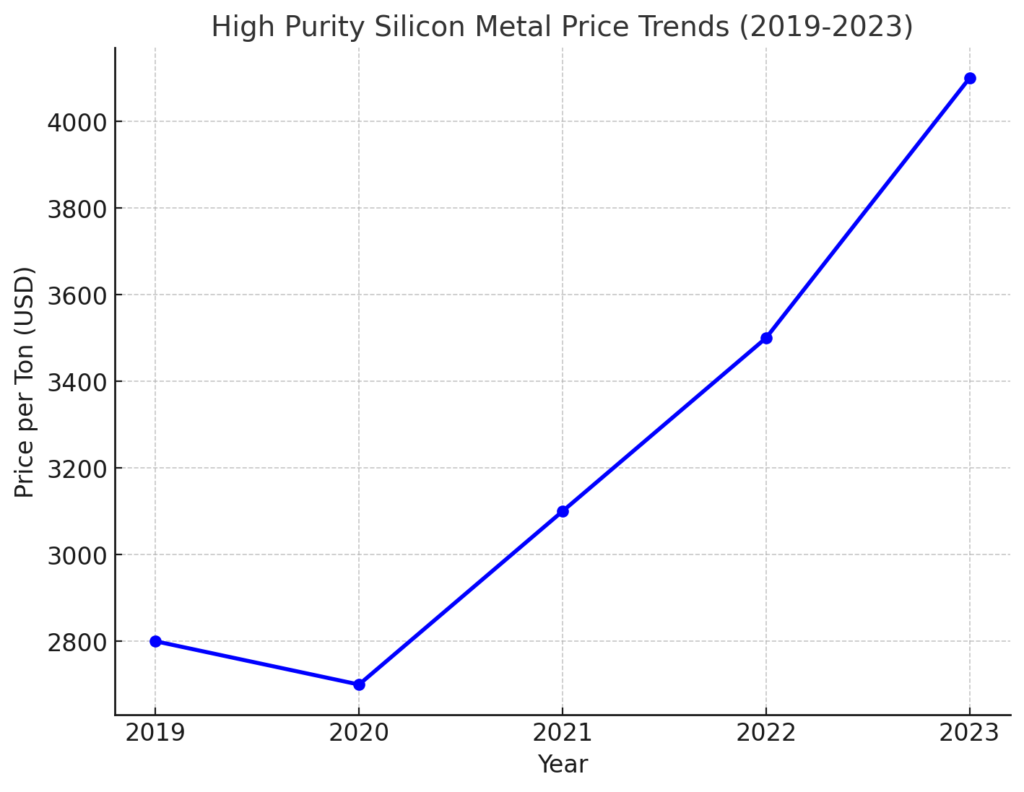
As of early 2024, 4N silicon metal was priced at about $2,800 per metric ton. That’s a 15% jump from the previous year. Supply chain issues and increasing demand are behind this price hike.
Big players in the market are gearing up. Companies like Ferroglobe, Elkem, and Wacker Chemie are investing heavily. Ferroglobe, for example, is putting $150 million into upgrading its facilities. They aim to boost high purity silicon production by 20% over three years.
Environmental Considerations
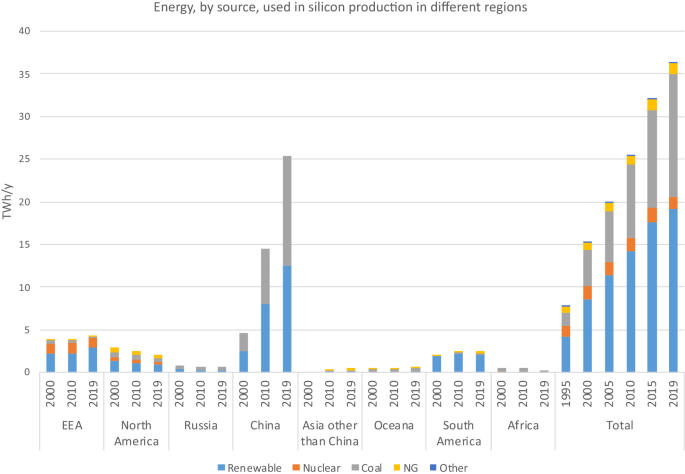
Let’s talk energy use. Producing a ton of silicon requires about 11 MWh of electricity. That’s a lot. But the industry is working on sustainability. Using hydroelectric power instead of coal-based electricity can cut the carbon footprint by up to 60%.
What This Means for You
If you’re in an industry that uses high purity silicon metal, keep an eye on these trends. Supply chain disruptions and growing demand could affect prices and availability. On the flip side, technological improvements might lead to more efficient production and potentially lower costs in the long run.
For investors, the high purity silicon metal sector offers interesting opportunities. But it’s not without challenges. Balancing increased production with environmental concerns will be key.
In Conclusion
High purity silicon metal production is a complex process that’s constantly evolving. As demand grows, driven by tech advancements and the push for renewable energy, the industry faces both challenges and opportunities. Staying informed about new purification techniques and shifts in global supply chains will be crucial for anyone involved in this dynamic market.
[Image of finished high purity silicon metal ingots or wafers]












